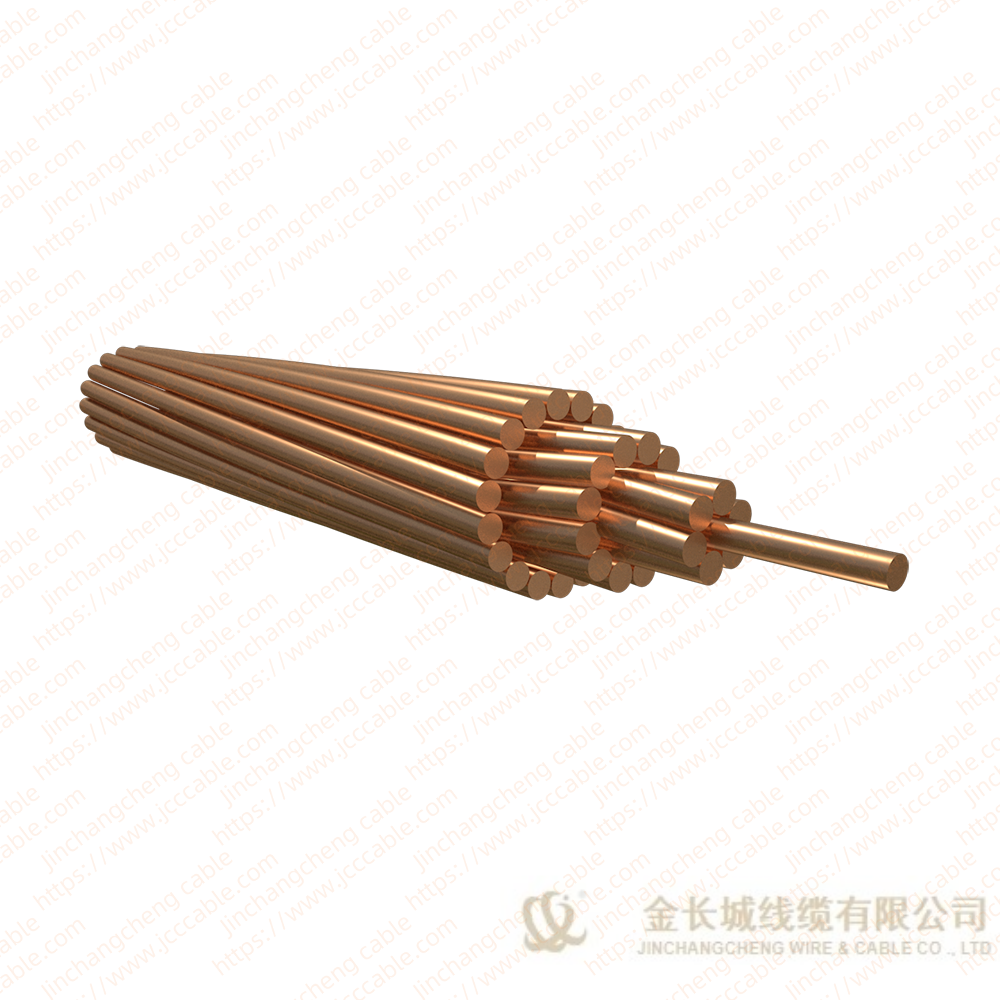
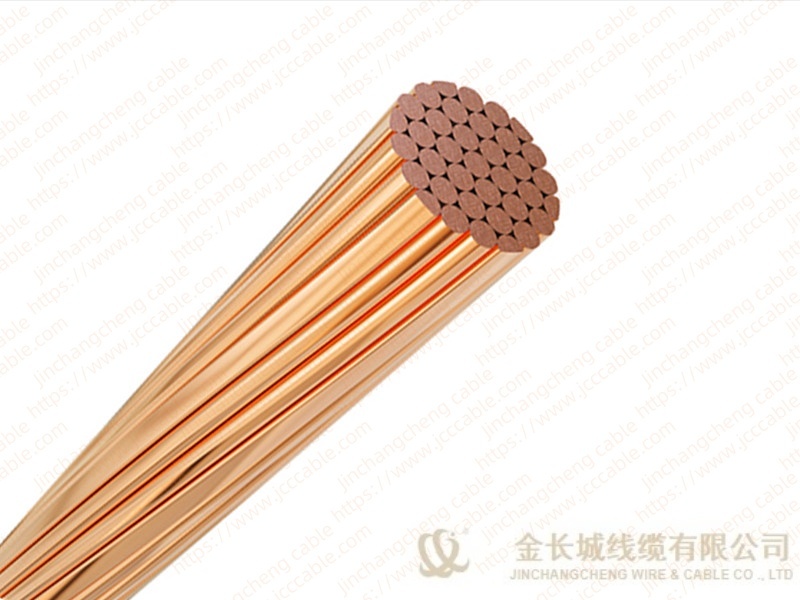
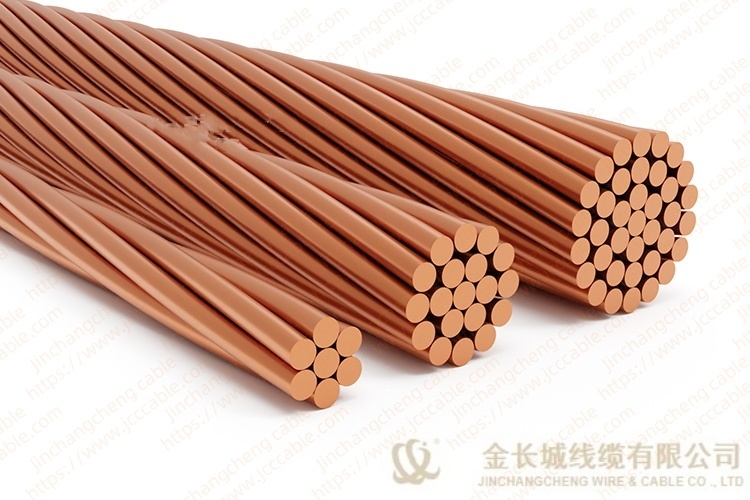
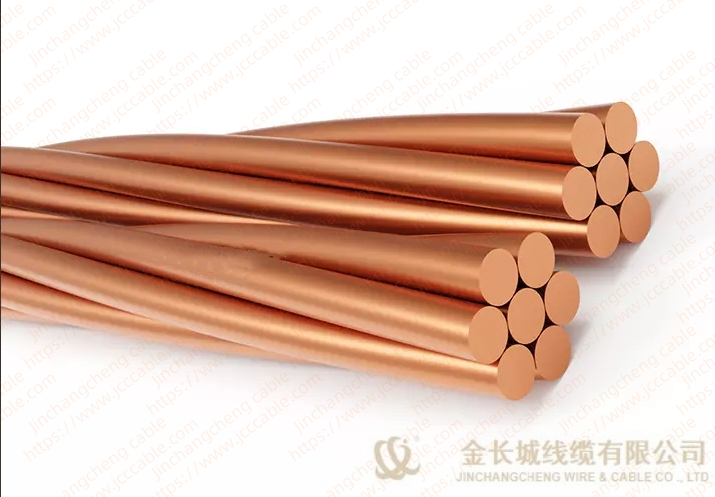
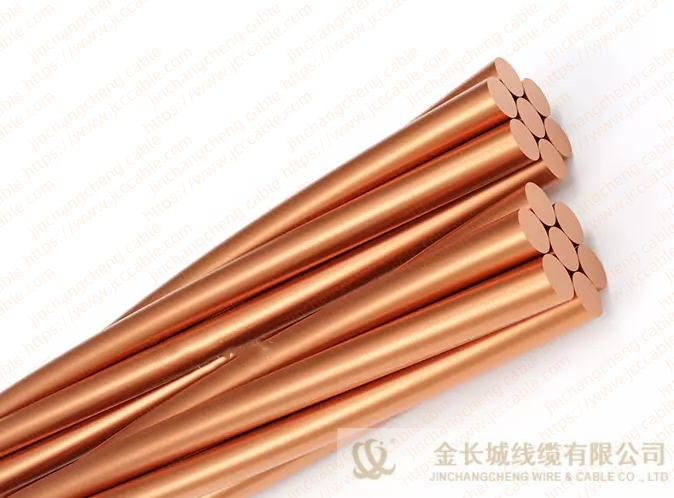
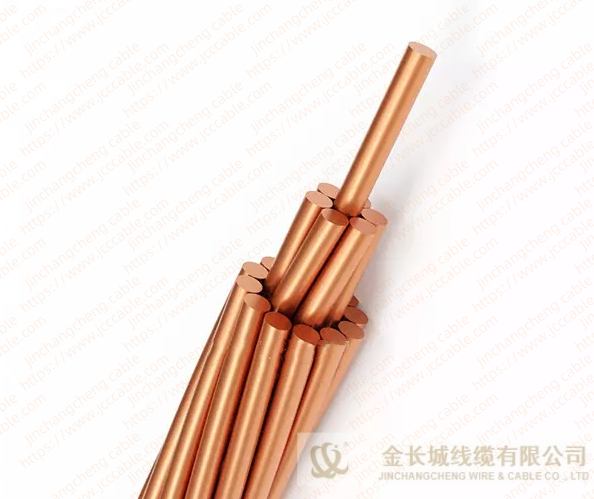
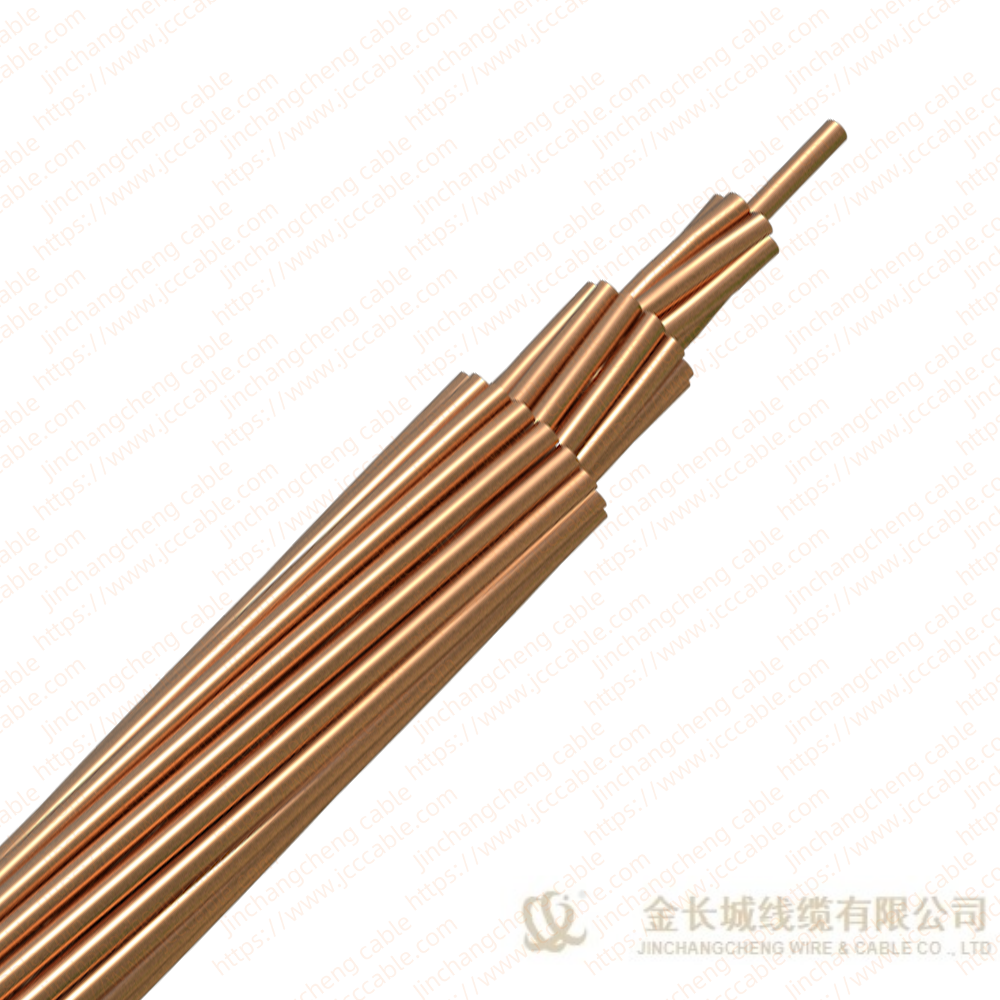
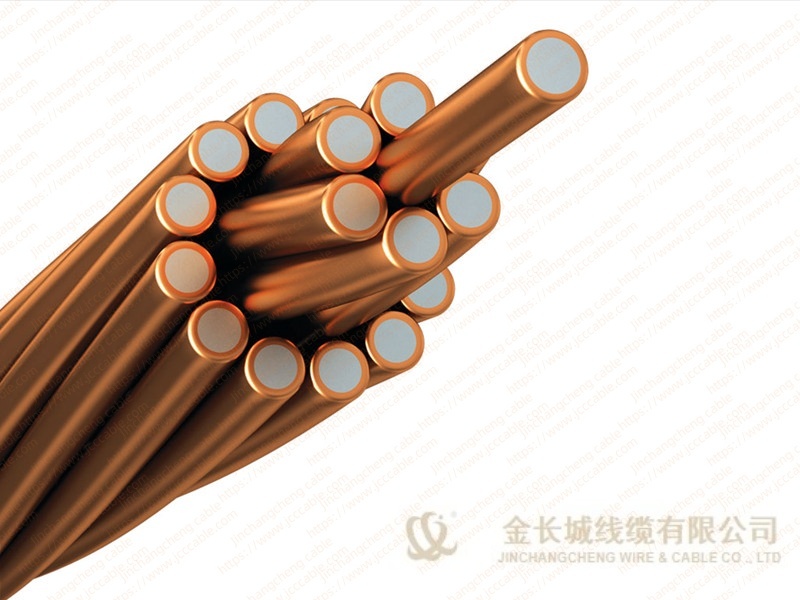
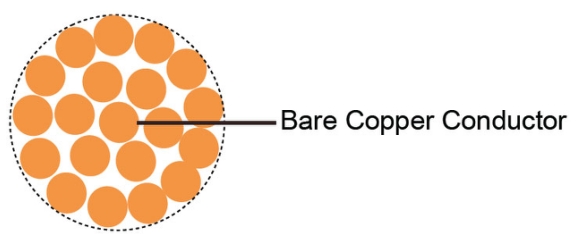
Bare copper stranded conductor
Classification:
Product Description
The bare copper strand conductor also are known as bare copper conductor, ground copper and bare copper strand. They have two main types, the hard drawn and soft drawn (tinned soft drawn).
The stranded bare copper is the connection of electrical equipment for transmission and distribution (such as transformer, the electric cabinet of the electric furnace), electronic and electrical equipment, and SCR components, and can also be used as ground wire for electrical operation.
Standard
BS EN 60228 / IEC 60228
Advantages:
Excellent conductivity: High-purity copper ensures low resistance of the wire and reduces energy loss.
Good flexibility: The twisted structure makes the wire flexible and easy to install and wire.
Strong corrosion resistance: Copper has good corrosion resistance and is suitable for a variety of environmental conditions.
High mechanical strength: The twisted design enhances the tensile strength of the wire and adapts to complex installation environments.
Product Features
High Tensile Strength
Hard drawn copper offers excellent resistance to mechanical stress, sagging, and breakage—ideal for long-span and overhead applications.
Stranded Flexibility
The concentric stranded design increases flexibility, making installation easier and improving resistance to vibration and bending stress.
Good Electrical Conductivity
While slightly lower than annealed copper, hard drawn copper still provides efficient power transmission for medium to high-voltage systems.
Corrosion Resistance
Bare copper provides natural resistance to corrosion, extending service life in outdoor and urban environments.
Low Maintenance
Suitable for applications where long-term durability and minimal maintenance are required.
Technical Infomation
Construction characteristics | |
Conductor material | Electrolytic, stranded and bare copper |
Conductor class | Class 2 according to BS EN60228 |
Usage characteristics | |
Minimum Installation Temperature | 0°C |
Maximum Installation Temperature | 60°C |
Minimum Operating Temperature | -15°C |
Maximum Operating Temperature | 70°C |
Maximum conductor temperature | 90°C |
Linear resistance @20°C | According to BS EN60228 / IEC 60228 |
Short-circuit max. conductor temperature | 370°C |
Mechanical characteristics | |
Min. Bending Radius | 35mm^2 up to 400mm^2 = 6 x OD |
Product structure and parameter
Solid
Size | Section | Number | Wire Diameter | Conducto | Resistance | Minimum | Minimum | Minimum Tensile | Total | |
AWG/MCM | Cmils | mm² | mm | mm | Q/km | % | kg/mm² | kg | kg/km | |
4 | 41740 | 21.1 | 7 | 1.96 | 5.88 | 0.865 | 1.1 | 46.4 | 883 | 192 |
2 | 66360 | 33.6 | 7 | 2.47 | 7.42 | 0.544 | 1.2 | 45.4 | 1373 | 305 |
1/0 | 105600 | 53.5 | 19 | 1.89 | 9.47 | 0.342 | 1.1 | 46.4 | 2234 | 485 |
2/0 | 133100 | 67.4 | 19 | 2.13 | 10.6 | 0.271 | 1.1 | 45.9 | 2785 | 611 |
4/0 | 211600 | 107.2 | 19 | 2.68 | 13.4 | 0.171 | 1.2 | 45.4 | 4379 | 972 |
250 | 250000 | 126.7 | 37 | 2.09 | 14.6 | 0.144 | 1.1 | 45.9 | 5231 | 1149 |
300 | 300000 | 152.0 | 37 | 2.29 | 16 | 0.120 | 1.1 | 45.9 | 6278 | 1379 |
350 | 350000 | 177.3 | 37 | 2.47 | 17.3 | 0.103 | 1.2 | 45.4 | 7243 | 1609 |
400 | 400000 | 202.7 | 37 | 2.64 | 18.5 | 0.090 | 1.2 | 45.4 | 8277 | 1838 |
500 | 500000 | 253.4 | 37 | 2.95 | 20.7 | 0.072 | 1.3 | 44.9 | 10230 | 2298 |
Class A
Nominal | Number | Overal | Maximum |
| Allowable | Cable | Standar |
mm | No./mm | mm | Q/km | kgf | A | kg/km | m |
10 | 7/1.35 | 4.05 | 1.8054 | 438 | 90 | 90 | 1000/R |
16 | 7/1.70 | 5.10 | 1.1385 | 694 | 125 | 143 | 1000/R |
25 | 7/2.14 | 6.42 | 0.7185 | 1076 | 160 | 227 | 1000/R |
35 | 7/2.52 | 7.56 | 0.5181 | 1459 | 200 | 314 | 1000/R |
50 | 7/3.02 | 9.06 | 0.3589 | 2095 | 250 | 452 | 1000/R |
50 | 19/1.78 | 8.90 | 0.3825 | 2021 | 250 | 428 | 1000/R |
70 | 19/2.14 | 10.70 | 0.2646 | 2921 | 310 | 618 | 1000/R |
95 | 19/2.52 | 12.60 | 0.1918 | 3961 | 380 | 858 | 1000/R |
120 | 19/2.85 | 14.25 | 0.1492 | 5067 | 440 | 1097 | 1000/R |
150 | 37/2.25 | 15.75 | 0.1238 | 6289 | 510 | 1334 | 1000/R |
Application
Power transmission: used for the erection of high-voltage and low-voltage power lines to ensure a stable power supply.
Electronic equipment connection: used for signal transmission and power connection inside electronic equipment to ensure the reliability of data transmission.
Building wiring: used for electrical wiring inside buildings to meet lighting and power needs.
Automobile and transportation: used in automobile and railway systems to connect electrical systems to ensure safe operation.
Product inquiry
We will contact you within one working day. Please pay attention to your email.
Related Products